The modern distributed workforce means the traditional network perimeter has become obsolete. With rapidly evolving digital estates, vulnerabilities are inevitably being exposed as cyberattackers look to capitalize on outdated security tools and protocols.
Today’s organizations need a new security model that more effectively adapts to the complexity of the modern environment, embraces the mobile workforce, and protects people, devices, apps, and data wherever they’re located.
The Challenges:
Provisioning corporate assets to support remote working arrangements.
Use of personal devices and email for business & handling sensitive information.
Enable remote workforces and close the security gap with Zero Trust security
What is Zero Trust?
Instead of assuming everything behind the corporate firewall is safe, the Zero Trust model assumes breach and verifies each request as though it originates from an open network. Zero Trust requires every access request, even those inside the organization’s enterprise network, to be fully authenticated, authorized, and encrypted before granting access. This “never trust, always verify” approach leverages advanced technologies to minimize lateral movement and detect and respond to anomalies in real time.
Zero Trust Principles

Always authenticate and authorize based on all available data points, including user identity, location, device health, service or workload, data classification, and anomalies.
Limit user access with just-in-time and just-enough-access (JIT/JEA), risk-based adaptive polices, and data protection to help secure both critical data and productivity.
Minimize impact and prevent lateral movement by segmenting access by network, user, devices, and app awareness. Verify all sessions are encrypted end to end.
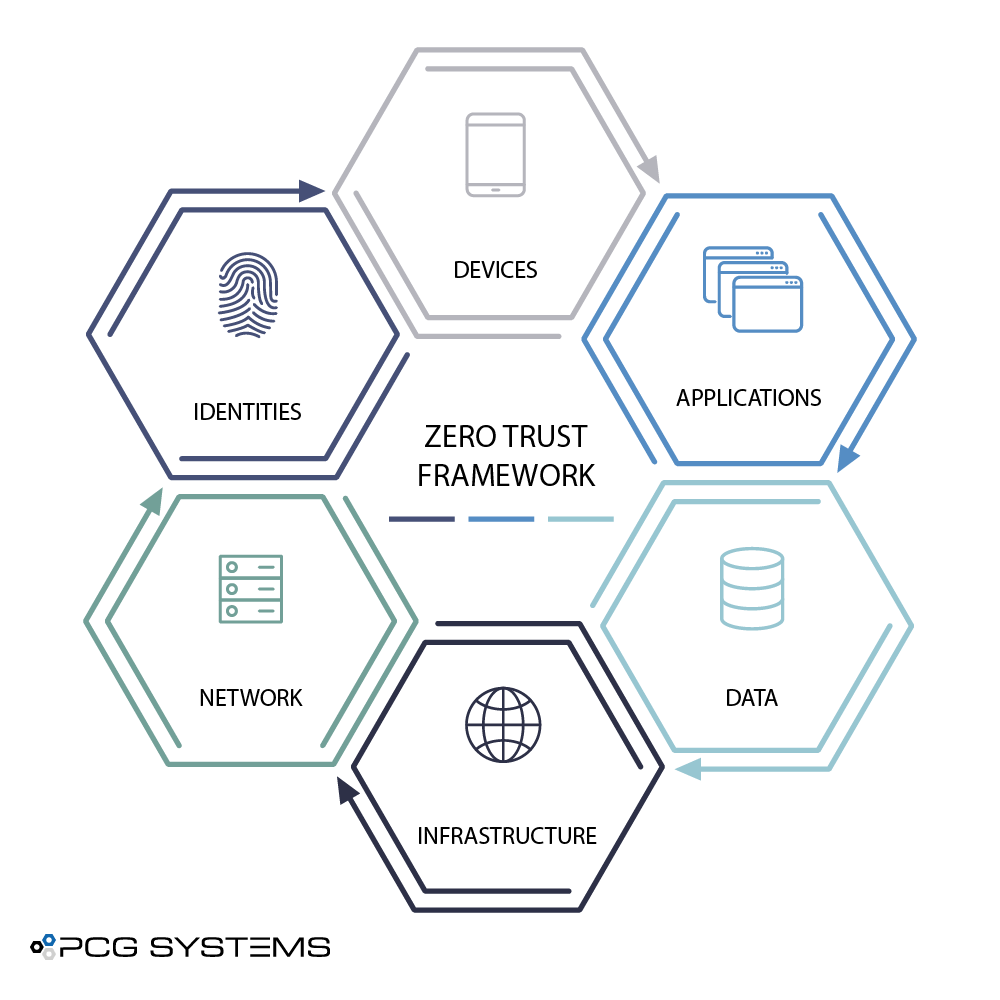
Zero Trust Components

IDENTITIES
Verify and secure each identity with strong, multi-factor authentication across your entire digital estate.
DEVICES
Gain visibility into devices accessing the network. Ensure compliance and health status before granting access.

APPLICATIONS
Ensure appropriate in-app permissions, gate access based on real-time analytics, monitor, and control user actions.

DATA
Move from perimeter-based data protection to data-driven protection. Use AI to classify & label data. Encrypt and restrict access based on organizational policies.

INFRASTRUCTURE
Use telemetry to detect attacks & anomalies, automatically block & flag risky behavior, and employ least privilege access principles.

NETWORK
Encrypt all internal communications, limit access by policy, and employ micro-segmentation and real-time threat detection.
Digital transformation forces re-examination of traditional security models
The old way of security does not provide business agility, user experiences, and protections needed for a rapidly evolving digital estate. Organizations implement Zero Trust to alleviate these challenges and enable the new normal of working anywhere, with anyone, at any time.
Why Zero Trust?
Empower your users to work more securely anywhere and anytime, on any device.
Enable digital transformation with intelligent security for today’s complex environment.
Adopting Zero Trust
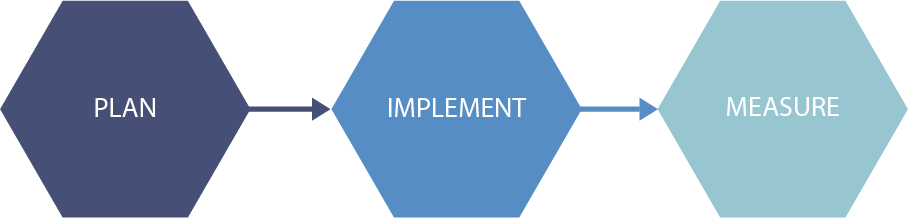
Although a Zero Trust security model is most effective when integrated across the entire digital estate, most organizations will need to take a phased approach that targets specific areas for change based on their Zero Trust maturity, available resources, and priorities.
Many organizations will benefit greatly from utilizing hybrid infrastructure that helps utilize existing investments and begin to realize the value of Zero Trust initiatives more quickly.
PLAN
Build a business case focused on the outcomes that are most closely aligned with your organization’s risks and strategic goals.
IMPLEMENT
Create a multiyear strategy for your Zero Trust deployment and prioritize early actions based on business needs.
MEASURE
Track the success of your Zero Trust deployment to provide confidence that the implementation of Zero Trust provides measurable improvements.
Key Investments
As you begin to assess your Zero Trust readiness and begin to plan on the changes to improve protection across identities, devices, applications, data, infrastructure, and networks, it will be important to consider each investment carefully and align them with current business needs. Key investments that help drive Zero Trust implementation more effectively include:
1. Strong Authentication
Ensure strong multi-factor authentication and session risk detection as the backbone of your access strategy to minimize the risk of identity compromise.
2. Policy-based Adaptive Access
Define acceptable access policies for your resources and enforce them with a consistent security policy engine that provides both governance and insight into variances.
3. Micro-segmentation
Move beyond simple centralized network-based perimeter to comprehensive and distributed segmentation using software-defined micro-perimeters.
4. Automation
Invest in automated alerting and remediation to reduce your mean time to respond (MTTR) to attacks.
5. Intelligence and AI
Utilize cloud intelligence and all available signals to detect and respond to access anomalies in real time.
6. Data Classification and Protection
Discover, classify, protect, and monitor sensitive data to minimize exposure from malicious or accidental exfiltration
Deploy Zero Trust at Your Organization
Get guidance on implementing Zero Trust principles across identities, endpoints, data, applications, networks, and infrastructure. Contact us today.